Unit1
Unit1
Topic: Data, Database and Database System
Learning Objectives:
- Data and Database.(Lecture-1)
- Introduction to Data Base Systems.(Lecture-2)
- Flipped Classroom.
- Homework.
Data & Database:
- Data: Collection of raw facts.
- Database: Organized collection of data for easy access & management.
- DBMS: Software for storing, managing, and retrieving data efficiently.
A Database Management System (DBMS) comprises several key components: 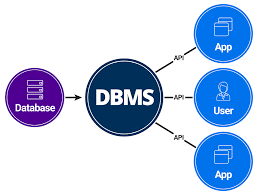
- Developer: Designs and maintains the database, ensuring efficiency and security.
- User: Interacts with the database to retrieve or input data.
- Application: Provides an interface between the user and the database, simplifying access to information.
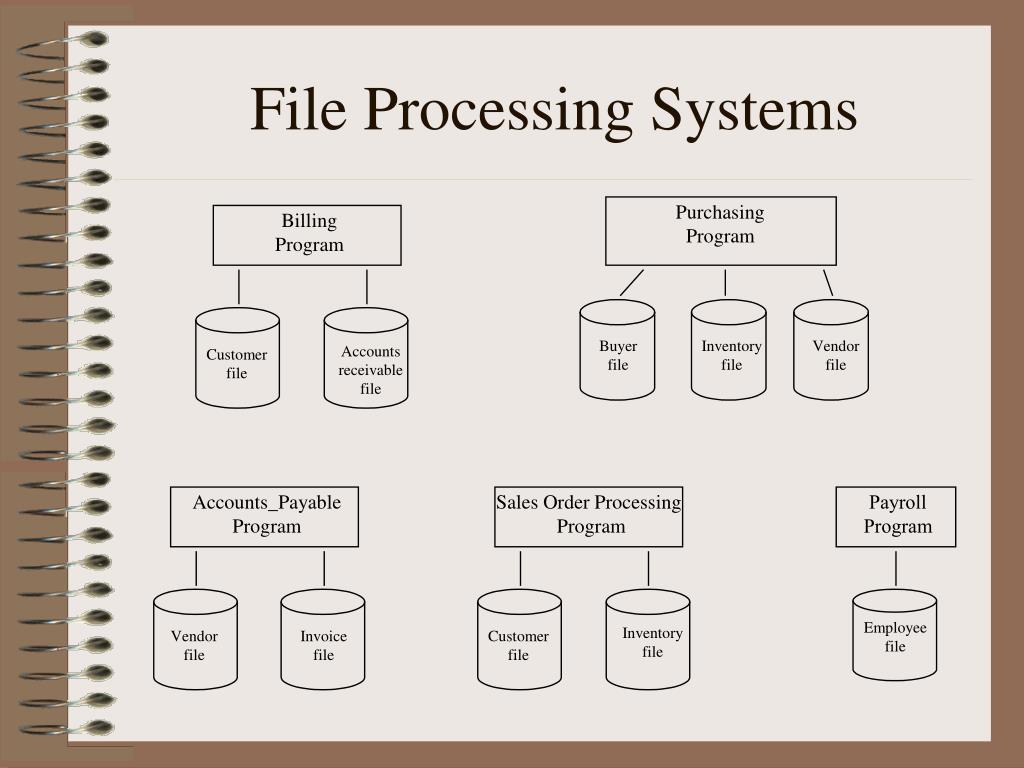
file-processing system(Traditional method)
Disadvantages of file-processing systems:
- Data Redundancy & Inconsistency: Duplicate data wastes storage and causes inconsistencies.
- Difficulty in Accessing Data: Lacks efficient querying and indexing.
- Data Isolation: Separate files hinder data integration and sharing.
- Integrity Issues: No validation, leading to incorrect or inconsistent data.
- Atomicity Issues: Incomplete transactions may leave data in an inconsistent state.
- Concurrent Access Anomalies: Multiple users can cause conflicts and data corruption.
- Security Risks: Weak access controls, encryption, and auditing make data vulnerable.
Advantages of DBMS:
- Data Consistency:
- Centralized updates prevent inconsistencies.
- Scalability:
- Handles large data & multiple users efficiently.
- Security:
- Controls access & protects data.
- Reduces Redundancy:
- Prevents duplicate storage using Normalization.
- Data Abstraction:
- Hides complexity, simplifies access..
Why Use a Database System?
Centralized Data Management: Reduces redundancy & inconsistency.
Improved Security: Protects sensitive data.
Efficient Access & Processing: Fast retrieval & updates.
Supports Multiple Users: Allows concurrent data access.
Scalable & Flexible: Can grow with the organization.
Data is the New Gold**
- In the digital era, data is as valuable as gold because it drives decision-making, innovation, and business success.
- Database systems help manage and organize vast amounts of data efficiently.
Brief History of Database Evolution
https://palden518.github.io/DBS101.github.io/2024/02/01/unit1.html
- Introduction to database system:
View of Data
- A DBMS supports database creation, querying, updating, and management based on a data model.
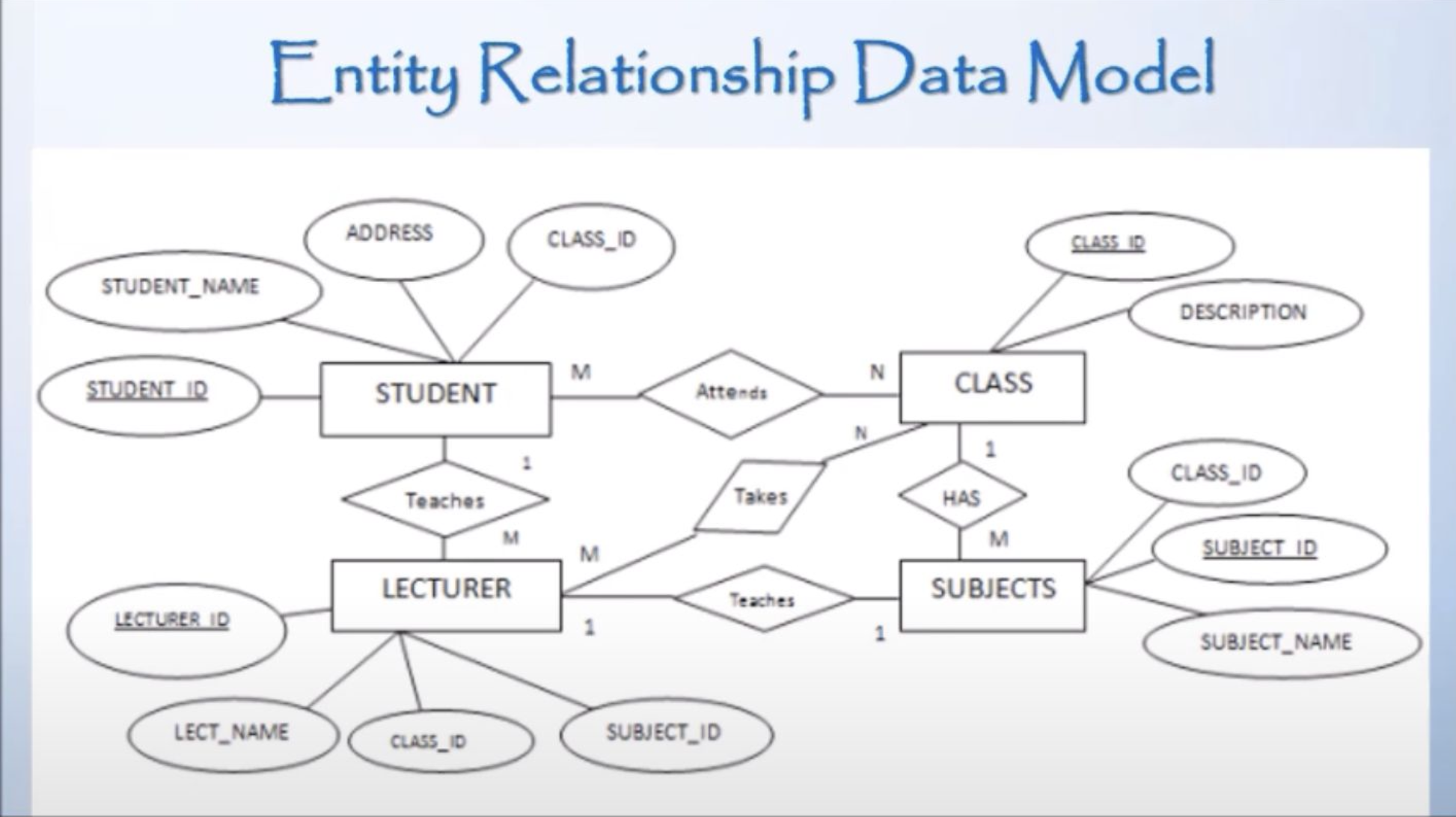
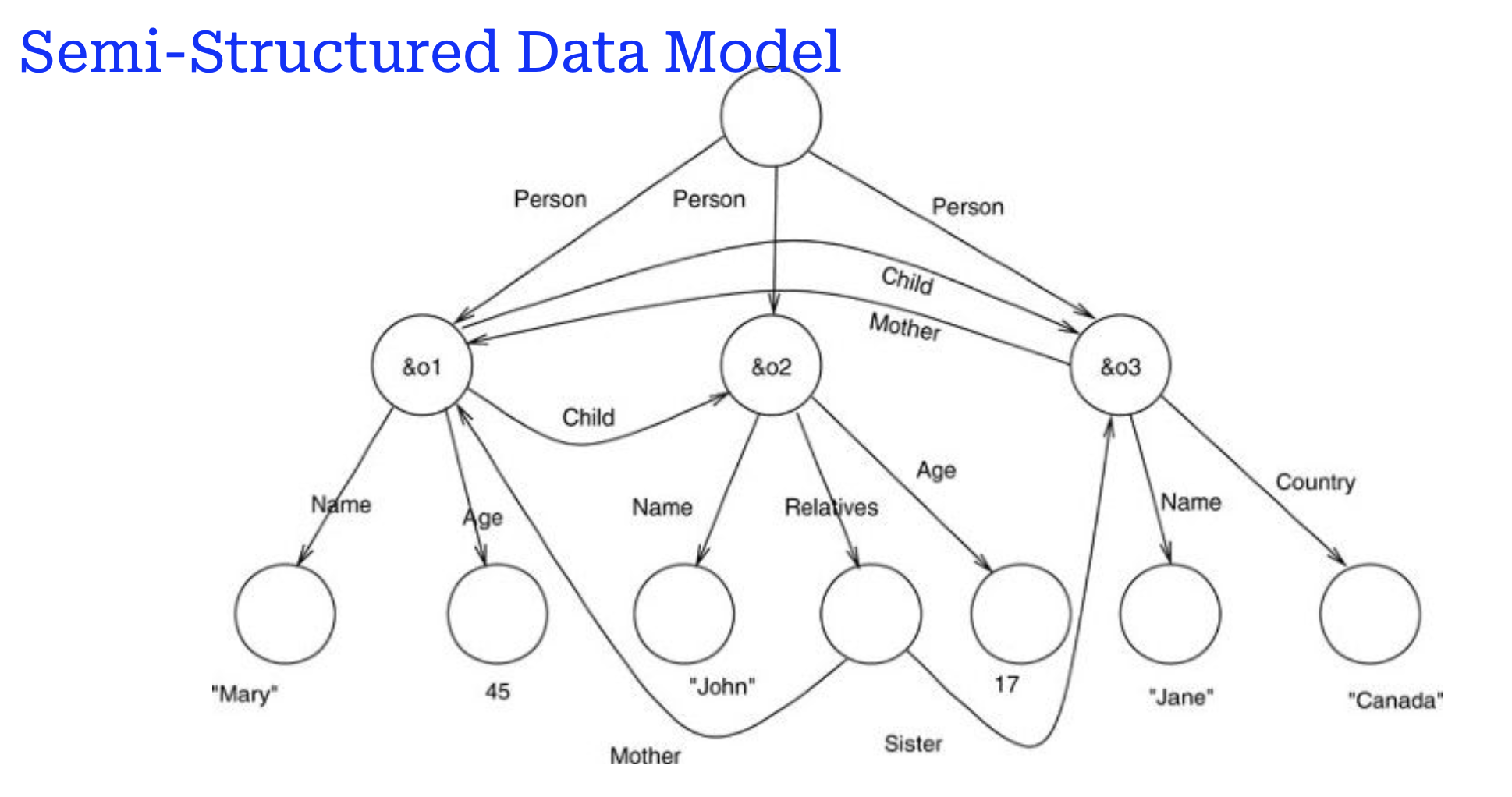
- Data Model: Defines the structure, relationships, meaning, and constraints of data.
Types of Data Models
- Entity-Relationship (ER) Model
- Semi-structured Data Model
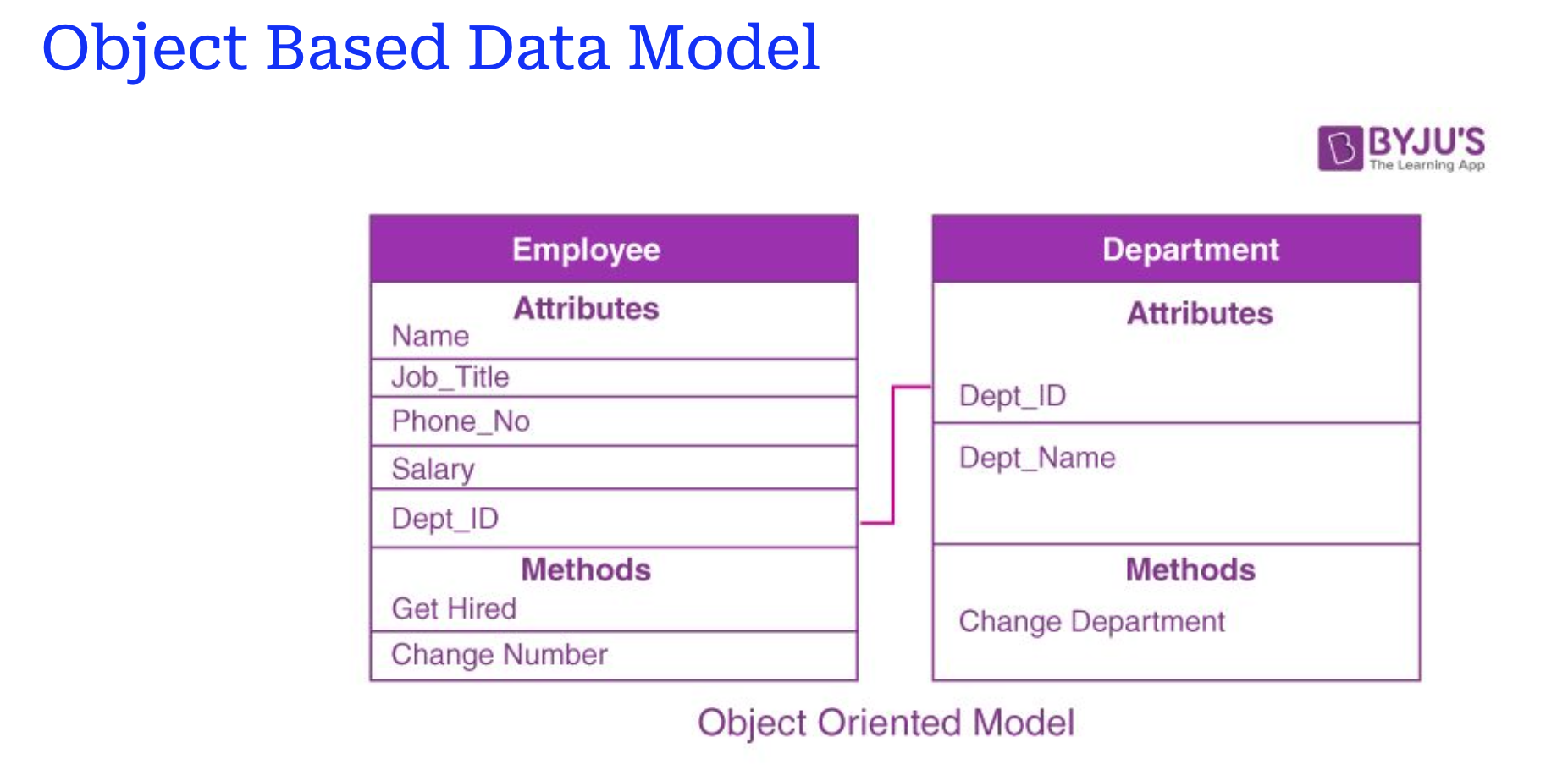
- Object-Based Data Model
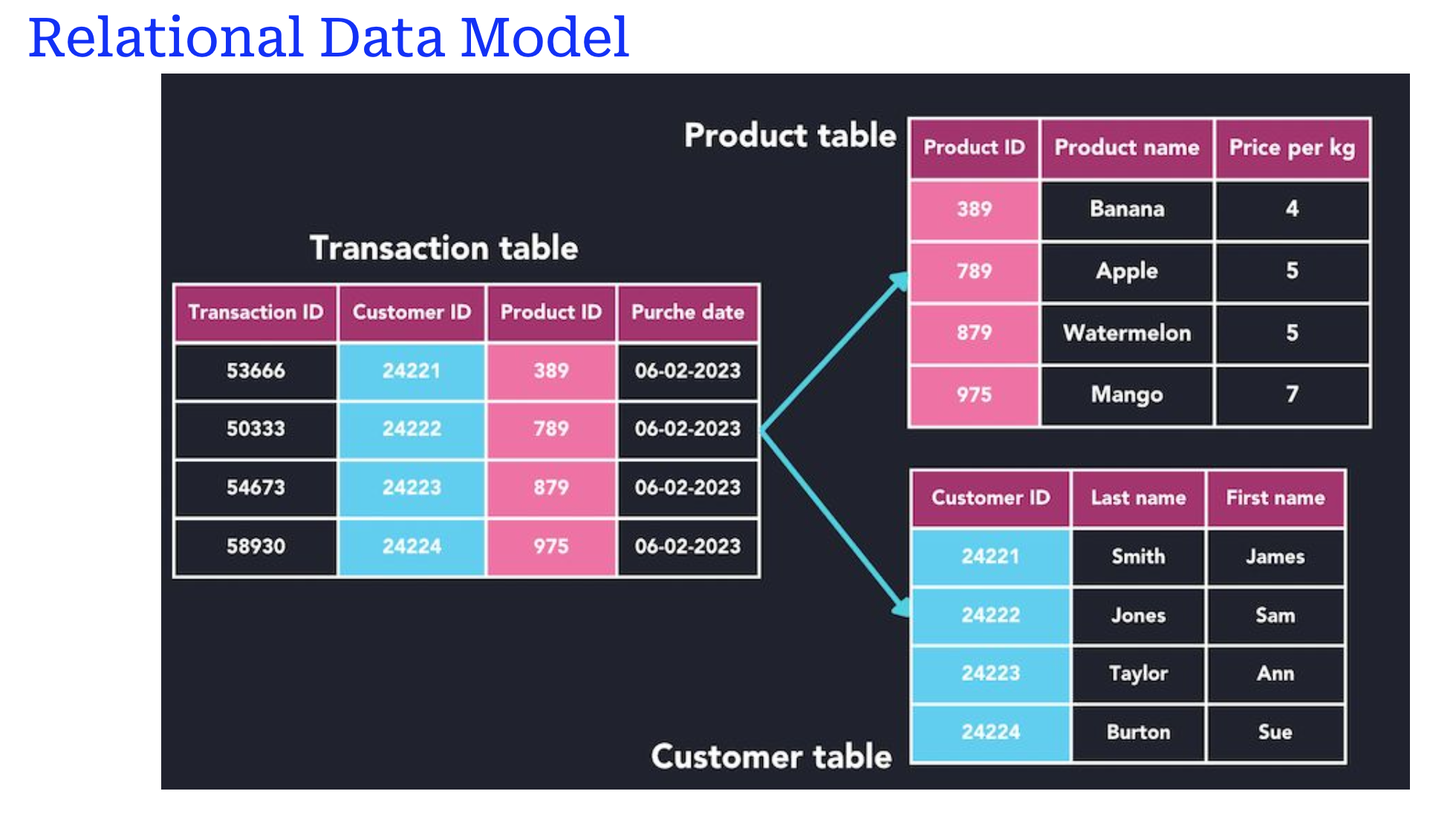
- Relational Model
Data Abstraction
- It hides the complexity of data structures from users, allowing easier interaction with the database.
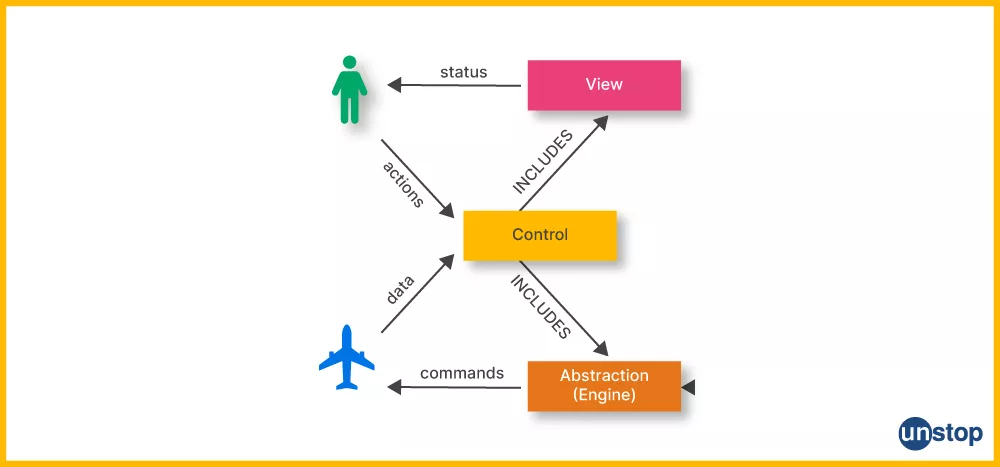
- Physical Level: Defines how data is stored internally (e.g., file structures, indexing).
- Logical Level: Describes what data is stored and the relationships between them.
- View Level: Shows only a part of the database, customized for different users.
Database Design Steps
- Select a Data Model: Choose the structure for organizing data.
- Conceptual Design: Define functional requirements and high-level schema.
- Logical Design: Map the conceptual schema to the database system.
- Physical Design: Optimize storage and access methods for performance.
Database Schema vs. Instance.
- Schema: Blueprint/structure of a database.
- Instance: Current data in the database.
Database Languages
- DDL (Data Definition Language): Defines schema (CREATE, ALTER, DROP).
- DML (Data Manipulation Language): Manages data (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
- Query Language: Retrieves data (SQL).
Database Engine
- A database engine is software in a DBMS that manages storage and handles CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
- It is also called a storage engine or embedded database.
- MySQL & MariaDB allow switching engines.
- PostgreSQL has a fixed built-in engine.
Database Engine Components
- Storage Manager: Manages data storage and connects low-level data with applications and queries.
- Query Processor: Includes DDL interpreter, DML compiler, and query evaluation engine to process queries.
- Transaction Management: Ensures safe and consistent execution of database transactions.
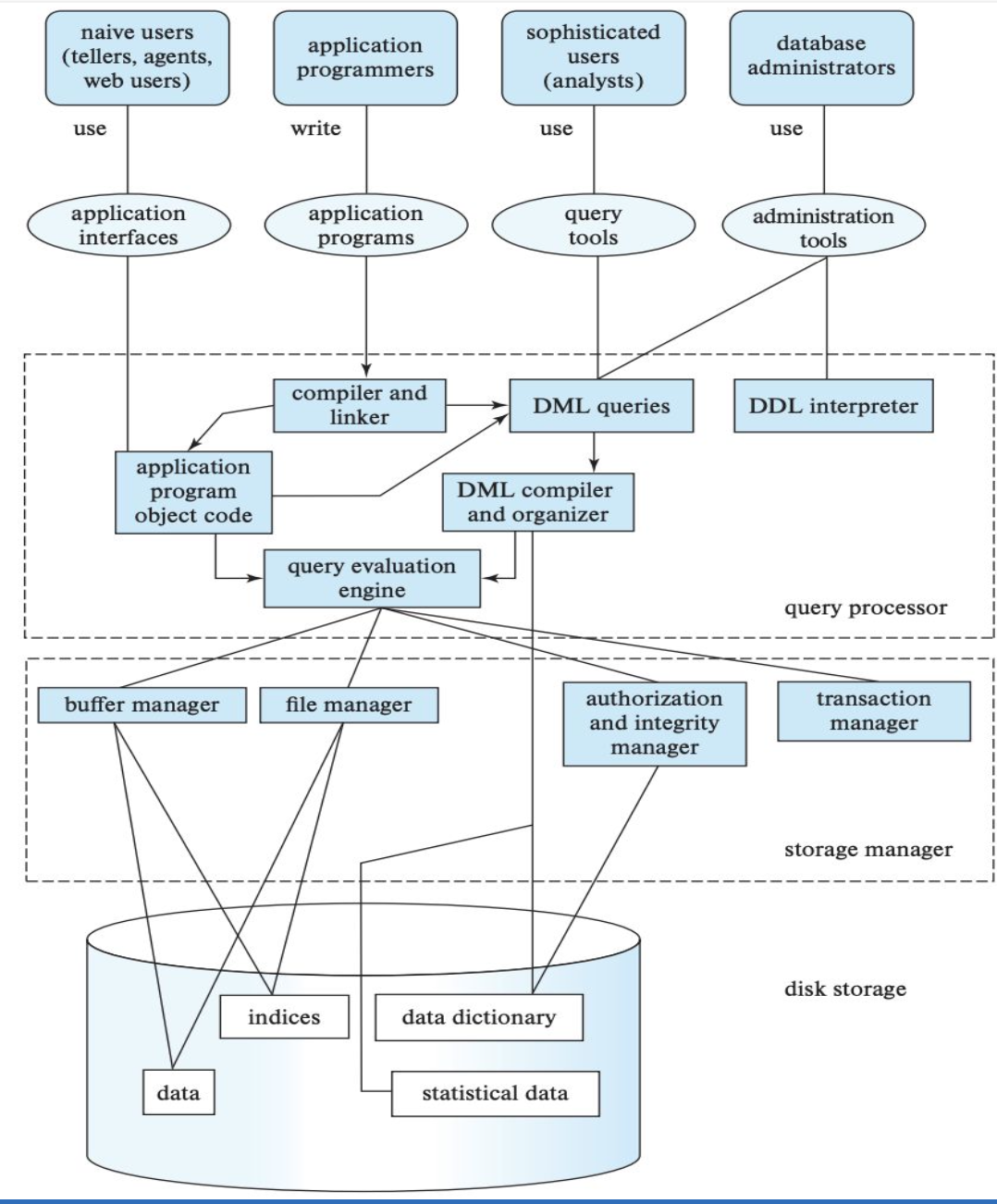
Database System Architecture:
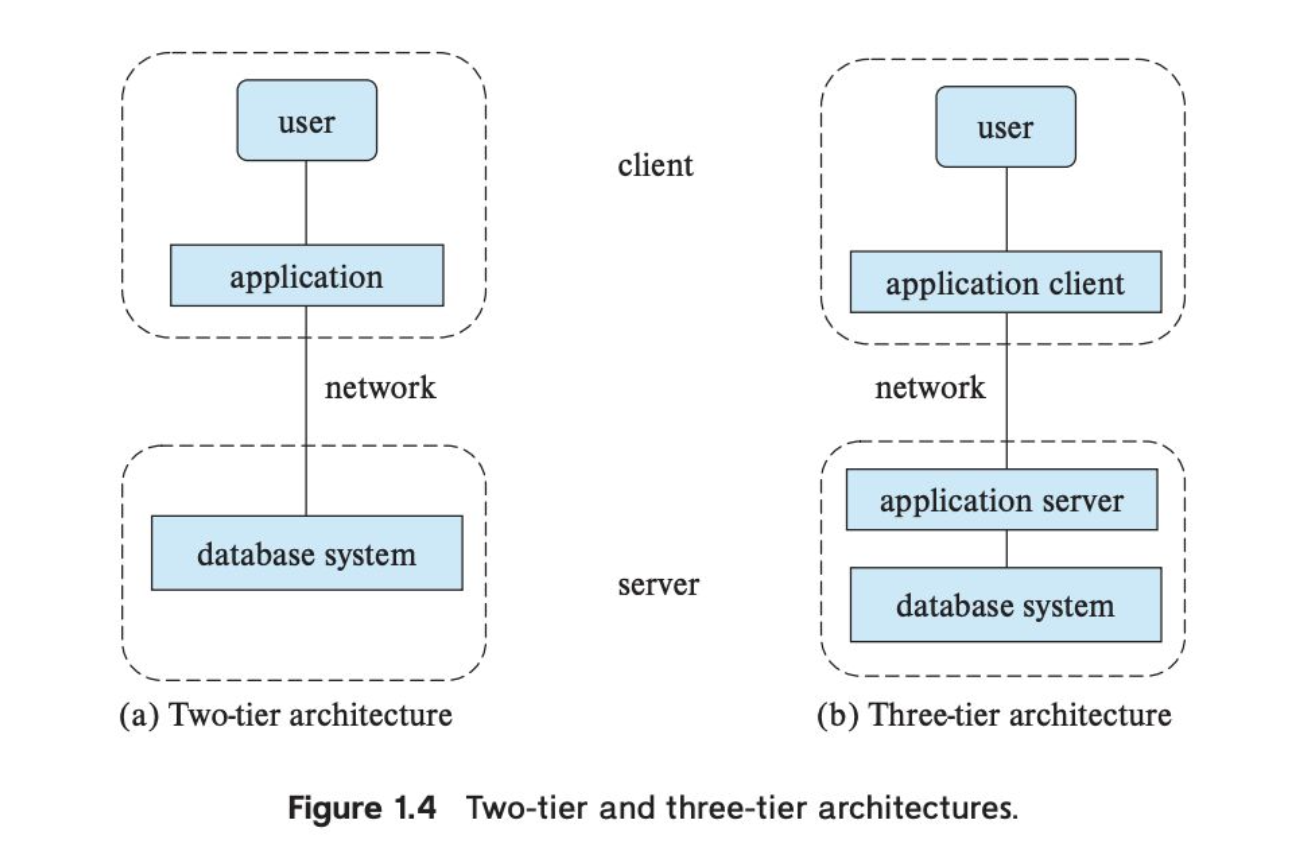
Architecture of Applications that use Databases as Backend:
Flipped Classroom:
What are the different types of database users and administrators
Types of Database users are:
- Database administrators(DBA):
- Manage the database system, set permissions, and ensure security.
- Example: A DBA who manages MySQL databases in an enterprise system.
- Appplication Programmers:
- Developers who write applications that interact with the database.
- Example: A software engineer coding a web app that fetches user data from a database.
- End Users:
- Regular users who interact with the database through applications.
- Consist of Naive and sophisticated User.
- Example: A student using a university portal to check grades.
- System Analysts:
- Design database structures and recommend database technologies.
- Example: An IT specialist designing an inventory database for a company.
- Database Designers:
- Define the database schema (tables, relationships, constraints).
- Example: A designer creating an ER model for a library system.
- Data Scientist And Analysts:
- Extract insights from data stored in databases using SQL queries or analytics tools.
- Example: A data scientist using PostgreSQL to analyze sales trends.
- Casual/Temporary Users:
- Users who occasionally run simple queries without deep technical knowledge.
- Example: A manager checking monthly sales reports in a business database
- Specialized Users:
- They interact with databases using automation, scripts, AI models, or ETL processes instead of manual queries, enabling advanced data processing and analytics.
Key Responsibilities of Database Administrators:
- Database Setup & Configuration:
- Install, configure, and maintain DBMS.
- Security & Access Control:
- Manage user permissions and protect data.
- Backup & Recovery:
- Ensure regular backups and disaster recovery plans.
- Performance Optimization:
- Tune queries, indexing, and caching for efficiency.
- Data Integrity & Consistency:
- Maintain accurate and consistent data.
- Database Maintenance:
- Apply updates, patches, and archive old data.
- User Management:
- Create and manage database users and roles.
- Troubleshooting:
- Identify and resolve database errors and slow queries.
- Automation & Scripting:
- Write scripts for backups and performance monitoring.
- Collaboration:
- Work with developers and analysts to optimize databases.
Home work:
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.